A lot of times when you're using Perl you have a list (or array), and you need to search that list for all strings that match a certain regular expression pattern (or regex). Fortunately Perl is built for this type of work, and it's straightforward to (a) perform this search, and (b) put your search results in another list.
Scala, Java, Unix, MacOS tutorials (page 399)
| The Bill Gates Bestseller | |

|
How to Avoid a Climate Disaster |
This isn't usually a place to discuss politics, but this is too cool for me to pass up, a chance to once again see Ron Howard play Opie from the Andy Griffith Show and Richie Cunningham from Happy Days. Even better, Howard's brief skit also includes Andy Griffith as Andy Taylor, and Henry Winkler reprising his role as the Fonz. It's pretty cool, I only wish it was longer and they were even more in character. (But hey, the wigs are funny.)
I got this Unix/Linux error message today "mv: cannot unlink '/tmp/forms-1.2.1.jar': Operation not permitted" when trying to move (mv) the file forms-1.2.1.jar from the /tmp directory to another directory. The full error output looked like this:
Java Swing FAQ: How do I increase the JScrollPane scrolling speed when using the mouse wheel?
Once you put a component (JTextArea, JEditorPane, JTable) into a JScrollPane in a Java Swing application, you'll quickly see that the default scrolling speed when trying to vertically scroll the viewport with the mousewheel is very slow. To make your scroll pane faster, i.e., more like a native Mac or Windows application, you'll want to increase this default mousewheel vertical scrolling speed.
When I work with Perl I’m often performing a task where I need to read from a text file, and many times all I have to do is read one record from the file. This happened again today, where I have a text file that just contains one pid (process id), and I just need to get that pid right before I do some other work.
For a Perl program that I'm working on right now, I need to match the elements of an array of strings against several patterns, and then take an action if the current string matches one of my patterns. This is pretty easy in this case, in part because it's easy to match a string against multiple patterns in Perl, and also because my patterns are very simple -- no regular expressions involved.
A frequently asked question Perl question is "How do I determine the size/length of a Perl array?", or the equivalent "How do I determine how many elements are in a Perl array?"
There are at least three different ways to do determine the Perl array size/length. Here's some Perl source code that shows these three Perl array size approaches:
Perl true/false FAQ: What is true in Perl? What is false in Perl?
The Perl programming language is a little unusual in not having true and false boolean operators. Because of this, I can never seem to remember what equates to true and false in Perl, so I decided to create this page.
What is true/false in Perl
In short, the following elements evalue to false in Perl:
Perl equality FAQ: Can you share a list of the Perl equality operators?
Sure. Here's a convenient list of the Perl comparison operators (also known as Perl equality operators, equal, or not equal operators).
The Perl comparison operators are different for numeric and string comparison tests, as you can see in the following table:
An interesting thing about developing software to work with an FTP server is that for some tests you need files to be uploaded to the FTP server very slowly. Usually you want software to run as fast as possible, but in my case I needed to be able to throttle the FTP upload speed to test portions of my code. (Specifically, I'm writing code to listen to Proftpd FTP server events, and I needed this to make sure all the STOR, DELE, RNFR, and RNTO events work as advertised (making sure the event notifications aren't sent until the event is complete.)
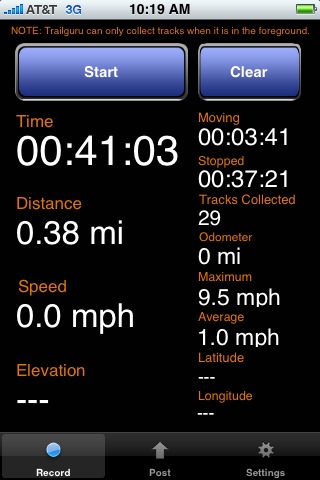
I downloaded an iPhone app named Trailguru recently, and was hoping to give a review of it, but I had no luck with it this morning. I walked a little more than 2.25 miles, but as this screenshot shows, Trailguru says I walked only 0.38 miles:
I've never bought any DRM protected (digital rights management) music, so although it's a well-known fact among techies, I didn't know until recently that you can burn DRM songs to a standard CD. The implication here is that once you've burned the DRM-protected song to CD, you can then rip it back as an MP3 file, which is the part that blows me away. Not much protection there, other than "security through obscurity".
Here's my Rule #1 for Project Managers, as looked at from the perspective of a software developer:
Show active interest in your project, and in the people that work on the project.
Okay, I know that seems obvious -- and I'm a little fired up about this right now -- but I've been amazed to work with project managers in the last few years who seem to have more important things to do outside of work than they have to do at work, and by this I only mean during the Monday through Friday, 8-to-5 time frame.
I'm not normally a big stored procedure user or developer, but since stored procedures are supported in MySQL 5.0 and beyond I thought I'd give them a spin. In this blog post I'll show you how to create a very simple MySQL stored procedure. It's not quite a "Hello, world" stored proc, but it's close.
In my previous tutorial on using the Java String format method ("Java sprintf") I showed how to use the format method of the Java String class to format strings and text output. That method works fine in many situations where you use the sprintf function in other languages, such as when you need to either concatenate strings, or print formatted output using something like Log4J.
MySQL date/time FAQ: How do I create a field in a MySQL database table that will default to the current date and time whenever a new record is inserted into my table?
Answer: Just define the field in your table as a timestamp field, and combine that with the default keyword and the MySQL now() function when you define this field in your database table.
The syntax for creating a MySQL timestamp field that defaults to the current date and time when creating a new database table looks like this:
I may have shown this before in other ways, but I wanted to take a moment to show how to use a MySQL database from the MySQL command line client. The basic command to work with an existing database is the use command, where you say something like this:
mysql> use my_database
For instance, if you have a database named orders, you would declare that you want to start working with it (use it) like this:
MySQL FAQ: How do I show the schema of a MySQL database table?
Answer: Use the desc command from the MySQL command line client.
For instance, in my current application I have a database table named orders, and when I need to see the schema for that table I show it with the desc command like this:
desc orders
The MySQL output looks like this:
Perl test data FAQ: How can I store some sample/test data with my source code in Perl?
Answer: With Perl it's very easy to store some sample data in the same file as your Perl source code. Assuming you're creating a "main" Perl program (not a Perl module) you can use the special __END__ operator, and then include your data after that operator, as shown in my sample code below. You can then access that data using the main::DATA operator inside of a while loop.
Here's a quick sample program:
Perl FAQ: How do I access the arguments that have been passed to my subroutine or function?
Answer: The special array @_ holds the values that are passed into a Perl subroutine/function, and you use that array to access those arguments. The first argument is represented by the variable $_[0], the second argument is represented by $_[1], and so on.
It may also help to know that number of elements passed in to your subroutine is given by the value of scalar(@_).
| The Bill Gates Bestseller | |

|
How to Avoid a Climate Disaster |