Posts in the “android” category
What I learned today, February 23, 2015 (mostly Android)
This is a collection of notes about what I learned today, February 23, 2015. Most of it is about Android.
I need to refresh my cursor data set before calling notifyDataSetChanged
When (a) adding, editing, or deleting items in a ListView and (b) using a CursorAdapter, I need to update my cursor object before calling notifyDataSetChanged.
I created this method, which I call from my fragment’s onResume method:
My Google Nexus 9 review (making the switch from iPad to Android)
My old iPad 2 was, well, old, and it’s slow speed was driving me crazy. So I decided to buy a new tablet, but when I made that decision I also decided to look around, and in short, I eventually decided to buy a Google Nexus 9. After a few days with it, here’s my review of the Nexus 9.
The Nexus 9 unboxing experience
The Nexus 9 unboxing experience was a non-experience. The Nexus 9 comes in a simple, unattractive box, and there’s nothing special about any part of the unboxing experience.
How to create a static array of strings in Android (example)
It turns out that it’s easy to create and use a static array of strings in Android. Of course you can do this in Java code, as I describe in my Java string array tutorial, but for Android I’m talking about doing this in XML.
In short, this is how you define a static string array in an Android XML file:
Android ActionBar example: How to create an options menu item
As Android programming goes, creating an options menu item/button in the Android ActionBar is fairly straightforward. In this brief tutorial I’ll demonstrate all of the steps needed to add a new menu item to the action bar.
1) Define the view/layout
The first step is to declare what the menu “view” is going to look like. This is very similar to defining other Android views, you do it with an XML layout file.
Android 5 Preferences tutorial (PreferenceScreen, PreferenceActivity, and PreferenceFragment)
Creating a Preferences screen in Android isn’t too hard. The website rominirani.com has a very good preferences tutorial that just needs a minor update for Android 5, as a piece of the code shown there has been deprecated.
To create an Android Preferences UI, just follow these steps:
A Moto 360 smartwatch + Android Wear review
A week or two ago Google put the first generation Moto 360 watch/smartwatch on sale for $99, and I was lucky enough to buy one before they went out of stock. It seems weird to write a review about an older piece of technology, but I actually like the watch much more than I expected to — despite a few bugs — so I thought I’d share what I’ve learned.
Android: FLiB, a free Fast Little Browser
FLiB is a fast, free internet browser for Android devices. Read on for more details ...
Android AsyncTask (REST client): A source code example
I just got back into using an Android AsyncTask, and it took me a little while to re-load the concepts in my head. I used AsyncTask’s a few years ago, but haven’t used them since.
To help remember how they work, I created a little AsyncTask example project, and I’ve included all of the source code for that project here. I’ll show all of the source code for my classes and configuration files, and then explain the code at the end.
My Android AsyncTask docs and examples (parameters, callbacks, executing, canceling)
I’ve currently written this document as a “note to self” about how the Android AsyncTask works. It’s currently incomplete, but if you want to know how an AsyncTask works, most of the answers are generally here. I provide documentation for most aspects of the AsyncTask, though my coverage of (a) updating progress/status and (b) canceling an AsyncTask is a little weak atm.
How to use the Android 7 split screen feature (tutorial)
Android 7 comes with a cool new “split screen” feature where you can look at two apps running at the same time. This little pictorial/tutorial shows how to use this split-screen feature.
Code snippets for rapid prototyping of Android Studio apps
This is a list of Android code examples I’m starting to allow me to create rapid prototypes of Android applications using Android Studio. This is a very early list, I hope to be adding many more Android code snippets over time.
A note about functional programming in Android
I spent some time last week working on an Android application, and with my newfound knowledge of functional programming (FP), I was trying to apply FP principles to my Android Activities and Fragments.
Android isn’t really meant for FP, but one thing I found that I could do is to move a lot of my business logic out of the Activities and Fragments and into separate classes, where I could often implement methods as static functions. The advantage of this is that it forces you to consciously pass variables in and out of those static functions, rather than mutating them as instance variables (think “global” variables) in your Activities and Fragments (which is a common way to handle them).
I don’t have a specific example I can share today, but when I can I’ll update this post to show specifically what I mean. In the meantime, if you try to move some of your logic out of your Activities and Fragments, I think you’ll see what I mean.
How to start the Android command line shell (adb)
Android FAQ: How do I start the Android command line tool (so I can interact with my Android emulator or device)?
You start the Android command line with the adb shell command:
$ adb shell
This makes at least two assumptions:
- You have the Android SDK installed.
- You have an Android emulator (or physical device) running.
When you start the adb shell, you'll see a very simple prompt that looks like this:
The Android “adb shell list files permission denied” error
As a brief note, today I tried to list the files in my Android application, which was running on a physical Android device — a Nexus 9 — with this adb shell command:
adb shell com.alvinalexander.mybrowser ls /data/data/com.alvinalexander.mybrowser
When I did that, I got an Android/ADB “permission denied” error.
The short story is that a solution to this problem is to run the same command, but with the run-as argument, like this:
adb shell run-as com.alvinalexander.mybrowser ls /data/data/com.alvinalexander.mybrowser
As a note to self, I confirmed this run-as command again in February, 2022, while working on a Flutter app:
adb shell run-as com.valleyprogramming.myapp ls /data/data/com.valleyprogramming.myapp/app_flutter
More information
The Android docs describe the run-as option:
Run commands on a device as an app (specified using the package name). This lets you run commands in
adbas if the app you specify is running the command (that is, you have the same device access that the app has), without requiring root access. This might be necessary when usingadbon a non-rooted device or an emulator with a Play store image. The app must be debuggable.
Related commands
I don’t have time to add much more to this right now, but one thing I’ll note is that if you have to run an ADB command where the file path has spaces in it, this command worked:
> adb shell run-as com.alvinalexander.mybrowser ls /data/data/com.alvinalexander.mybrowser/app_webview/Web\\ Data
Android emulator not loading my app
I haven't used Android in a little while now, in particular with my new laptop, and the first time I tried running an Android app from inside Eclipse, the Android emulator wouldn't finish starting properly and run my app.
I remember I used to look under the "all apps" icon, and could sometimes find my app was actually loaded, but in this case, it wasn't loaded at all.
My “Just Be” app running on a Moto 360 (Android Wear)
(Click the image for a much larger image.)
Some time in the last week or two Google announced a $99 sale on their first generation Moto 360 watches. I purchased one, and it came in the mail this morning. My main purpose for buying one is to see how my “Just Be” mindfulness reminders app (for Android) works with Android Wear smartwatches. This image shows what the notifications currently look like.
I like the way it works off the shelf, but I kinda want to get rid of the “Just Be” name on the notification. The watch shows the app icon, and that’s good enough for me. I know it probably should be there for “branding” purposes, but I’d rather just see the mindfulness reminder message. At least the app name is in a much lighter font color, that’s good.
FWIW, I don’t have an Android phone, but I do have a Google/Android Nexus 9 tablet, and everything between the tablet and watch seems to be working fine so far.
(The Moto 360 watches were available at this link on the Google Play store, but the last time I checked they were out of stock.)
Just Be, a mindfulness reminder application
Today I’m proud announce that I’ve written an Android application named “Just Be”:
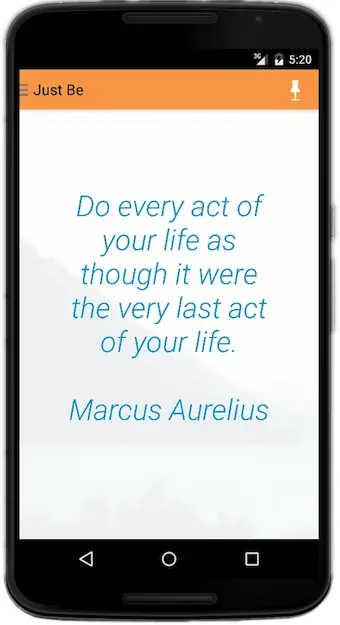
Just Be is a simple but useful “mindfulness reminders” app that helps bring you back to the present moment.
To use Just Be, all you have to do is a) configure the reminders that you want to see, b) optionally add your favorite background images, and c) set a notification schedule, and Just Be will send you notifications (mindfulness reminders) on that schedule.
I’d write more about it here, but I’ve already written about it at JustBe.cc, so please see that website for more information, including a short video.
How to delete/uninstall an Android app from an emulator from the command line
I recently had a problem with an Android emulator, and for some reason I wasn't able to delete the Android app I was developing. I knew you could delete Android apps from the command line, but I had no need to do this until now.
After reading a few docs, I found that I could delete my Android app from the command line using the adb command, like this:
Android/Java: How to get your app’s root data directory
If you ever need to get the root data directory of your Android application (app) from within your Java code, I can confirm that this approach works:
File rootDataDir = getActivity().getFilesDir();
When I log that directory like this:
Log.i(TAG, rootDataDir.toString());
it prints this output for my application:
/data/data/com.alvinalexander.mynewapp/files
where com.alvinalexander.mynewapp is the package name for my new Android app.