By Alvin Alexander. Last updated: February 3, 2017
The JOptionPane showOptionDialog is generally pretty straightforward, so without any introduction, here's the source code for a quick JOptionPane showOptionDialog example:
public void handleQuit()
{
// display the showOptionDialog
int choice = JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null,
"You really want to quit?",
"Quit?",
JOptionPane.YES_NO_OPTION,
JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE,
null, null, null);
// interpret the user's choice
if (choice == JOptionPane.YES_OPTION)
{
System.exit(0);
}
}
As you can guess, this simple handleQuit method does the following:
- Prompts the user with a JOptionPane showOptionDialog.
- If the user clicks the "Yes" button, our program is ended
Here's what this JOptionPane.showOptionDialog dialog looks like when it is displayed:
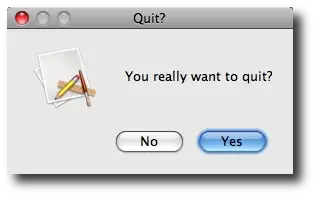
Controlling the JOptionPane showOptionDialog prompts
If you want to control the prompts that are shown to the user (the buttons), you can easily add your own labels to the buttons, as shown in this JOptionPane showOptionDialog example:
public void handleQuit() throws IllegalStateException
{
// display the showOptionDialog
Object[] options = { "OK", "Cancel" };
int choice = JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null,
"You really want to quit?",
"Quit?",
JOptionPane.YES_NO_OPTION,
JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE,
null,
options,
options[0]);
// interpret the user's choice
if (choice == JOptionPane.YES_OPTION)
{
System.exit(0);
}
}
As you can see, the rest of the showOptionDialog code is the same, and you just provide your desired options as an Object array.



